Dec . 18, 2024 18:41 Back to list
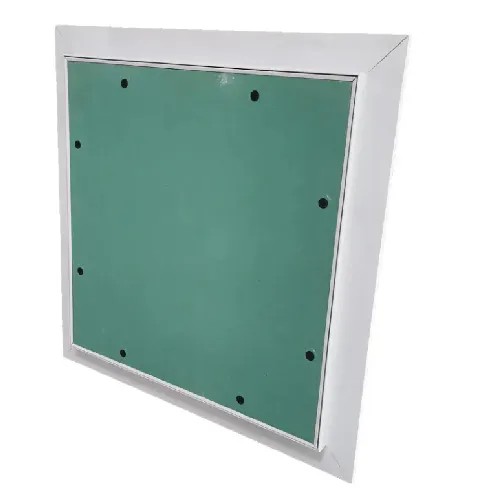
access panel sizes ceiling
Understanding Access Panel Sizes and Their Ceilings
Access panels are essential components in the construction and building maintenance sectors, serving as access points to various systems within walls, ceilings, and floors. Examples include plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. The design and installation of access panels must consider various factors, particularly their sizes and the ceilings they are associated with. In this article, we will explore the significance of access panel sizes, the designated standards, and the impact they have on building functionality and aesthetics.
Importance of Access Panel Sizes
Access panels are available in various sizes to accommodate specific applications. The size of an access panel largely depends on the system it is meant to service. For instance, larger panels may be necessary for accessing substantial mechanical equipment or ductwork, while smaller ones may suffice for electrical junction boxes. Selecting the correct size is crucial for efficient maintenance and emergency access, allowing professionals to reach necessary components quickly and safely.
Additionally, the size of the access panel affects the structural integrity of a building. Panels that are too small may lead to difficulty in accessing critical components, resulting in costly repairs or prolonged downtimes. Conversely, oversized panels can weaken the surrounding structure and compromise aesthetic appeal. It's essential to adhere to industry standards and regulations when determining the dimensions of access panels.
Standards and Regulations
The building code often dictates the acceptable sizes of access panels based on their intended use. For instance, the International Building Code (IBC) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) provide guidelines for access panel sizes, especially concerning fire-rated walls and ceilings. Compliance with these standards is critical, as failure to do so can result in safety hazards and legal ramifications.
access panel sizes ceiling
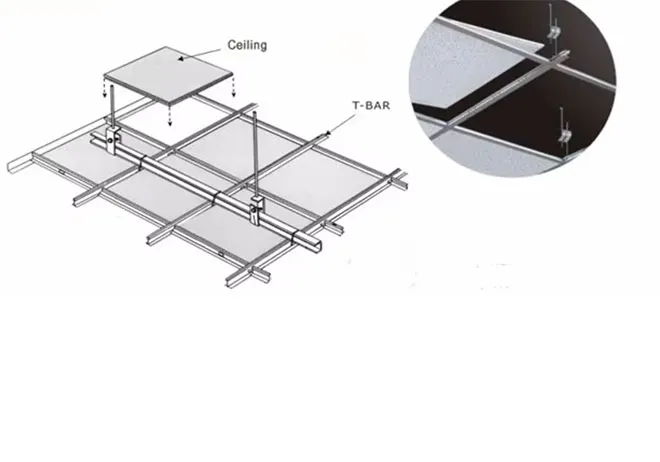
Moreover, specific sectors may have additional regulations. For example, hospitals may mandate larger access panels in critical areas to ensure that medical maintenance personnel can swiftly address issues with HVAC or electrical systems. In residential settings, the sizes might be dictated by functionality, as access points should blend seamlessly with the design of the space.
The Role of Ceilings in Access Panel Sizing
Ceiling types play a significant role in determining the size and style of access panels. For instance, suspended ceilings, commonly used in commercial buildings, often incorporate access panels designed to fit within the grid system. These panels should be unobtrusive yet functional, maintaining the aesthetic appeal of the ceiling while providing necessary access.
On the other hand, solid ceilings may require differently sized panels. In these cases, the access point must be designed with careful consideration of the surrounding materials to ensure a clean finish. Additionally, ceilings with different heights and structural complexities could necessitate specialized access panel sizes to adapt effectively.
Conclusion
Access panel sizes are a vital consideration in the design and maintenance of buildings. Properly sized access panels facilitate easy and efficient access to critical systems while adhering to safety regulations. The integration of these panels within ceilings, whether suspended or solid, further emphasizes the importance of meticulous planning in the construction process.
Understanding these dynamics not only ensures compliance with building codes but also promotes a smoother maintenance experience for professionals. In light of these factors, builders and architects must prioritize both functionality and aesthetics, ensuring that access panels serve their purpose without compromising the overall design and integrity of the space. Embracing a comprehensive approach towards the sizing and installation of access panels is, therefore, key to achieving a successful and sustainable construction project.
-
Quality Ceiling Trap Doors & Access Panels | Easy & Secure AccessNewsAug.30,2025
-
Durable Ceiling T Grid Systems | Easy InstallationNewsAug.29,2025
-
PVC Gypsum Ceiling: Durable, Laminated Tiles for Modern SpacesNewsAug.28,2025
-
Pvc Gypsum Ceiling Is DurableNewsAug.21,2025
-
Mineral Fiber Board Is DurableNewsAug.21,2025
-
Ceiling Tile Clip Reusable DesignNewsAug.21,2025







