ceiling access panel
Links
- The Versatile Power of 3M Self-Adhesive Amalgamating Tape
- Insulation Tape Blue A Versatile and Essential Tool for Electrical Work
-
Self-fusing silicone electrical tape finds applications across various industries. In electrical installations, it is commonly used for insulating splices, protecting wiring, and securing cables in both residential and commercial projects. Its resistance to heat makes it an ideal choice for high-performance applications, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors.
 They invest heavily in research and development to produce tapes with improved performance characteristics, such as higher heat resistance, better adhesion, or increased durability They invest heavily in research and development to produce tapes with improved performance characteristics, such as higher heat resistance, better adhesion, or increased durability
They invest heavily in research and development to produce tapes with improved performance characteristics, such as higher heat resistance, better adhesion, or increased durability They invest heavily in research and development to produce tapes with improved performance characteristics, such as higher heat resistance, better adhesion, or increased durability electrical tape manufacturers. Some manufacturers also focus on eco-friendly alternatives, using sustainable materials and production methods to minimize environmental impact.
electrical tape manufacturers. Some manufacturers also focus on eco-friendly alternatives, using sustainable materials and production methods to minimize environmental impact. Rubber tape edge sealant: application, advantages and disadvantages
The effectiveness of insulation tape hinges on several key characteristics
Moreover, yellow electrical tape is not limited to professional electricians; DIY enthusiasts can also benefit from its various applications. From home improvement projects involving lighting fixtures to securing cords and cables, the tape is an affordable and effective solution for numerous applications. The ease of use and accessibility of yellow tape makes it a staple in households and workshops alike.

butyl tape rubber.
In 1845, a surgeon named Dr. Horace Day made the first crude surgical tape by combining India rubber, pine gum, turpentine, litharge (a yellow lead oxide), and turpentine extract of cayenne pepper and applying that mixture to strips of fabric. It was the first “rubber-based” adhesive and Dr. Day used it in his practice as a surgical plaster. Larger scale manufacturing of similar medical tapes began in 1874 by Robert Wood Johnson and George Seaburg in East Orange, NJ. That company would soon become the Johnson & Johnson Company we know today. Later in 1921, Earle Dickson who bought cotton for Johnson & Johnson noticed that the surgical tape kept falling off his wife Josephine’s fingers after cutting them in the kitchen. He fixed a piece of gauze to some cloth backed tape and the first Band-Aid ® was invented. It took almost 75 years from Dr. Day’s first crude tape until the early 1920’s when the first industrial tape application appeared. The application was electrical tape (although the adhesive was more of a cohesive film than the electrical tape we know today) to prevent wires from shorting. The second major industrial tape application was a result of the rise of the American automobile in the 1920’s. Two-toned automobiles were becoming popular and automakers needed a way to produce clean, sharp paint lines while using the new automatic paint spray gun. They started using the surgical tape that was available but the paint wicked through the cloth backing and caused defective paint jobs. Richard Drew, an engineer at Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing (3M) happened to be at a local body shop testing their WetorDry® brand sandpaper in 1925 and he saw the workers struggling to get clean paint lines. He went back to his lab and created a 2-inch wide crimp backed paper tape that became the first “masking tape” for painting. Jumping ahead to 1942 and World War II, Johnson & Johnson developed duct tape to seal canisters and repair equipment for the military. The tape was a basically a polyethylene coated cloth tape with good “quick stick” properties that made it easy to use in the field for emergency repairs. The world never looked back and duct tape can be found in almost any home or toolbox.
Each of these adhesive types have advantages and disadvantages which make them more or less suitable for particular applications. Here we will draw the major lines outlining these differences.
One of the primary uses of amalgamating rubber tape is in the electrical industry. Electricians rely on this tape to provide insulation and protection for electrical connections and wires. The tape can be easily stretched and wrapped around the exposed wires, creating a tight and secure seal that prevents moisture and dirt from compromising the connection. Additionally, the tape's elasticity allows it to expand and contract with the wires, ensuring a long-lasting and reliable solution.
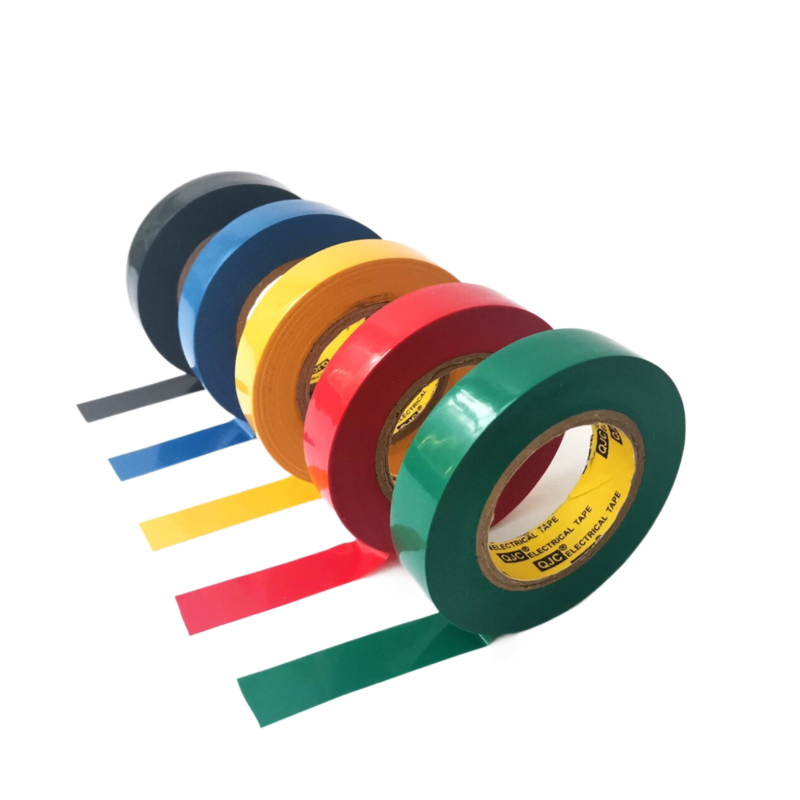
Electrical tape is an adhesive tape that is used specifically for electrical phasing and wiring jobs. Used as a safety measure, electrical tape is applied to any wires or cables which will conduct electricity, to protect and insulate them. Electrical tape is available in different types, depending on the material it is made from, including cloth electrical tape, mastic electrical tape, vinyl electrical tape, rubber electrical tape, and PVC electrical tape.
 This variety also enables artists to experiment with different styles and techniques, fostering creativity and innovation This variety also enables artists to experiment with different styles and techniques, fostering creativity and innovation
This variety also enables artists to experiment with different styles and techniques, fostering creativity and innovation This variety also enables artists to experiment with different styles and techniques, fostering creativity and innovation flex tape 12 x 10.
flex tape 12 x 10.  It is widely used in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, and oil refineries to seal and protect vital infrastructure It is widely used in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, and oil refineries to seal and protect vital infrastructure
It is widely used in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, and oil refineries to seal and protect vital infrastructure It is widely used in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, and oil refineries to seal and protect vital infrastructure fireproof adhesive tape. In construction, it is applied to building materials to increase fire resistance and comply with stringent safety regulations.
fireproof adhesive tape. In construction, it is applied to building materials to increase fire resistance and comply with stringent safety regulations. High voltage self-fusing rubber tape is a non-adhesive tape crafted from a blend of rubber and synthetic materials. Its unique self-fusing properties allow the tape to bond with itself when wrapped around an object, creating a solid, flexible, and waterproof seal. Unlike traditional tapes, the self-fusing nature eliminates the need for adhesive, making it an outstanding choice for high-temperature and high-voltage environments where reliable insulation is crucial.
Rubber tapes repel moisture and are a great solution for outdoor applications or in manholes where water may occasionally seep in.
Insulation tape is an essential tool in various industries, including electrical work, construction, and even home repairs. Often used to insulate electrical wires and prevent short circuits, it is designed to withstand certain temperatures and conditions. However, if you’ve ever looked to purchase insulation tape, you might have noticed a range of prices that can be quite perplexing. In this article, we will explore the factors influencing insulation tape prices and provide insights to help you make informed purchasing decisions.

