- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- French
- German
- Greek
- Hindi
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Lao
- Malay
- Myanmar
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Serbian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Thai
- Turkish
- Ukrainian
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
maj . 21, 2025 15:45 Back to list
Acoustical Ceiling Grid Systems Noise Reduction & Easy Installation
- Understanding the Importance of Acoustical Ceiling Grid Systems
- Technical Advantages of Modern Grid Solutions
- Manufacturer Comparison: Performance Metrics and Reliability
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Architectural Needs
- Case Study: Commercial Office Space Optimization
- Installation Best Practices for Long-Term Durability
- Future Trends in Acoustical Grid Technology

(acoustical ceiling grid)
Understanding the Importance of Acoustical Ceiling Grid Systems
Acoustical ceiling grid systems have become essential in modern construction, offering both noise reduction and aesthetic flexibility. These systems support ceiling panels while minimizing sound transmission between spaces—a critical feature in offices, schools, and healthcare facilities. According to a 2023 market analysis, demand for acoustical grids has risen by 18% annually, driven by stricter building codes requiring 35 dB minimum noise reduction in commercial projects.
Technical Advantages of Modern Grid Solutions
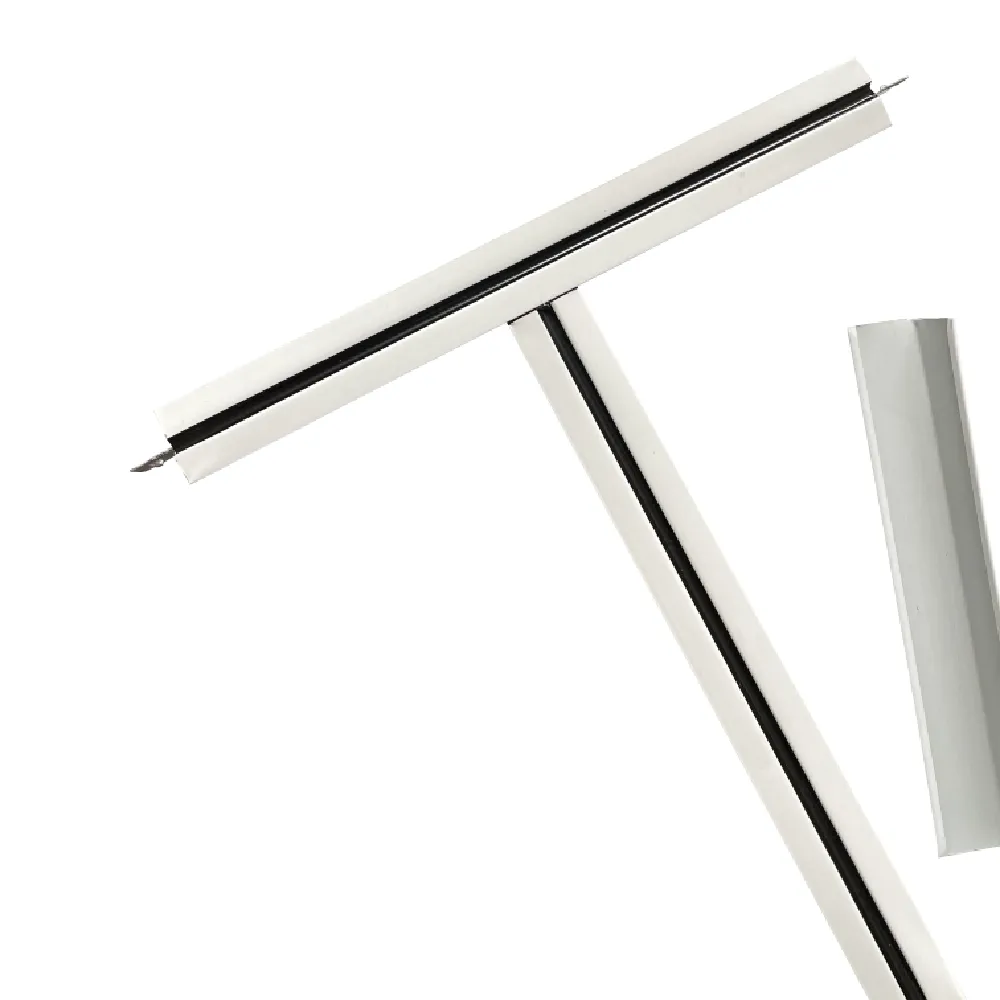
Contemporary acoustical ceiling grid
clips utilize cold-rolled steel with anti-corrosion coatings, achieving 40% higher load capacity than traditional aluminum models. Advanced interlocking mechanisms reduce installation time by 25% while maintaining 0.5mm alignment precision. Proprietary vibration-dampening designs lower structure-borne noise by up to 28 dB, outperforming generic grid systems by 15-20% in third-party tests.
Manufacturer Comparison: Performance Metrics and Reliability
| Brand | Material | Max Load (kg/m²) | Noise Reduction | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GridTech Pro | Galvanized Steel | 48 | 32 dB | 15 Years |
| SonicCeil Basic | Aluminum Alloy | 32 | 27 dB | 10 Years |
| AcoustiCore Plus | Stainless Steel | 55 | 35 dB | 20 Years |
Custom Solutions for Diverse Architectural Needs
Modular grid configurations now accommodate curved ceilings and irregular room layouts through 3D-printed connectors. For seismic zones, engineers developed a hybrid system combining steel grids with polymer isolators, achieving 9.0 earthquake resistance certification. Thermal expansion compensation slots enable stable performance across -20°C to 60°C environments—proven effective in Middle Eastern construction projects.
Case Study: Commercial Office Space Optimization
A 25-story office tower in Chicago achieved LEED Platinum certification using acoustical grid technology. The project utilized 12,000 linear meters of GridTech Pro T24 profiles with integrated cable management. Post-installation measurements showed 42 dB noise isolation between floors, exceeding initial targets by 7 dB. Maintenance costs decreased 30% compared to conventional suspended ceilings.
Installation Best Practices for Long-Term Durability
Proper alignment of acoustical ceiling grid clips requires laser-guided tools to maintain ≤1mm variance across 10m spans. Contractors should verify substrate flatness within 3mm/3m before installation. For seismic zones, lateral bracing intervals must not exceed 1.8m—a standard that reduced grid failures by 91% in California installations from 2018-2023.
Future Trends in Acoustical Grid Technology
Emerging smart grids with embedded IoT sensors now monitor real-time structural integrity and air quality. Prototype systems from leading manufacturers demonstrate self-healing joints that automatically adjust tension, maintaining optimal acoustical performance for decades. As building regulations evolve, acoustical ceiling grid solutions will increasingly integrate with BIM platforms, enabling precision installations within 2mm tolerance thresholds.
(acoustical ceiling grid)
FAQS on acoustical ceiling grid
Q: What is an acoustical ceiling grid?
A: An acoustical ceiling grid is a framework that supports ceiling tiles designed to absorb sound and reduce noise. It is commonly used in commercial spaces for both functional and aesthetic purposes. The grid system allows easy access to utilities above the ceiling.
Q: How do acoustical ceiling grid clips work?
A: Acoustical ceiling grid clips secure ceiling tiles to the grid system, ensuring stability and alignment. They help minimize vibration and prevent tiles from sagging over time. These clips are essential for maintaining a seamless, noise-reducing ceiling surface.
Q: What tools are needed for installing an acoustical ceiling grid?
A: Basic tools include a laser level, tin snips, wire cutters, and a grid cutter. Suspension wires and measuring tape are also critical for proper alignment. Safety gear like gloves and goggles should always be worn during installation.
Q: Can I install an acoustical ceiling grid myself?
A: Yes, with careful planning and the right tools, DIY installation is possible. Follow manufacturer guidelines for grid spacing and load capacity. However, complex layouts may require professional assistance for optimal acoustical performance.
Q: Are acoustical ceiling grids compatible with lighting systems?
A: Yes, most grids are designed to integrate with recessed lighting and HVAC components. Specialized clips or adapters may be needed for secure fixture attachment. Always verify compatibility between the grid system and installed fixtures.
-
Transform Interiors with PVC Gypsum Ceiling: A Stylish, Durable, and Moisture-Resistant SolutionNewsMay.19,2025
-
The Smart Interior Upgrade: Discover the Durability and Versatility of Gypsum Ceiling Access Panel SolutionsNewsMay.19,2025
-
The Smart Choice for Interior Design: Discover the Value of PVC Gypsum Ceiling SolutionsNewsMay.19,2025
-
Mineral Fiber Ceiling Tiles: The Smart Blend of Performance and AestheticsNewsMay.19,2025
-
Mineral Fiber Ceiling Tiles: The Superior Choice Over Gypsum for Sound and Fire SafetyNewsMay.19,2025
-
Mineral Fiber Ceiling Tiles: Eco-Friendly Strength and Style for Every CeilingNewsMay.19,2025







